Learn more about our Resistors portfolio
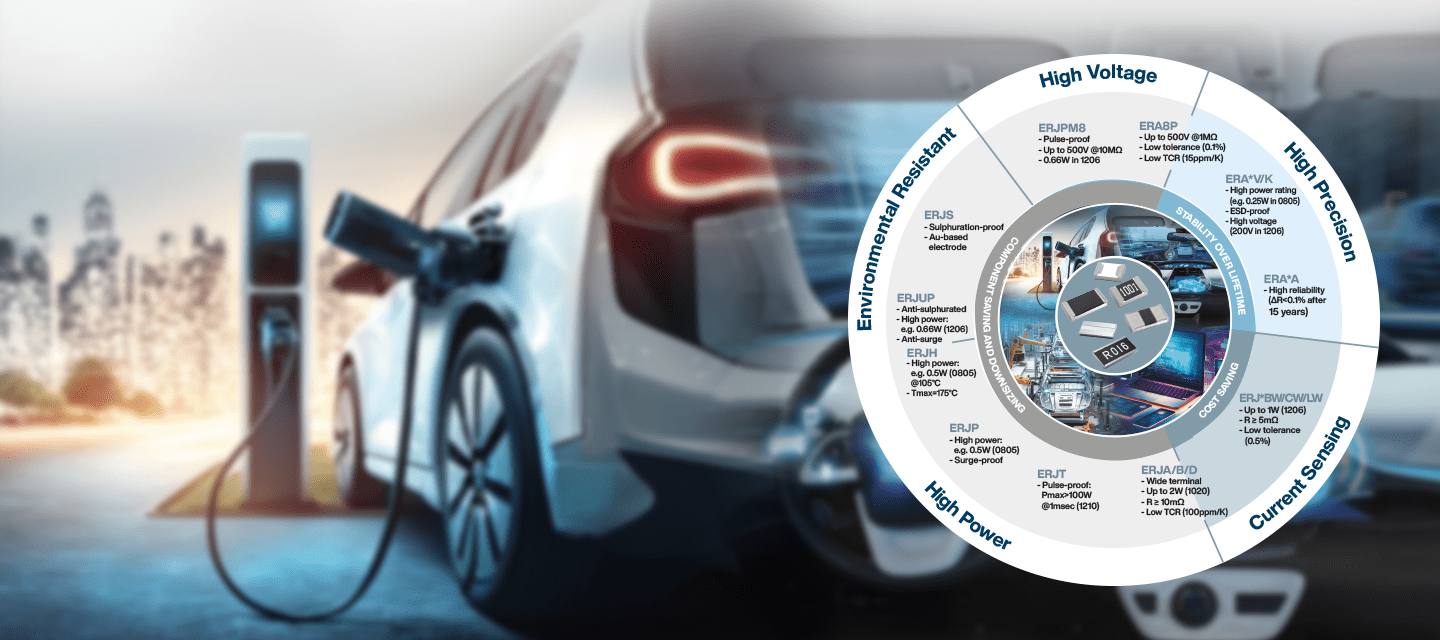
With over 90 years of resistor manufacturing experience, Panasonic offers a wide range of high-performance resistors to meet market needs. Resistors limit electric current and are essential in all electronic devices.
Panasonic's portfolio includes various types, from miniaturized chip resistors to high-power, high-precision, and specialized resistors for harsh environments.
Designed for reliability and stability, they support applications in automotive, industrial, and outdoor settings, helping to achieve miniaturization, cost savings, and high performance.
High performance chip resistors
Resistors are key components found in all electronic devices. Panasonic resistors are available in high precision, environment resistant, current sensing, small & high power.
Overview of our chip resistors
| Product | Part number | Spec Size (inch) | Power Rating (W) | Resistance (Ω) | Resistance Tolerance (%) | Datasheet | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Precision | Thin Film | ERA*A | 0201 to 1206 | 0.05 to 0.25 | 10 to 1M | ±0.05 to ±0.5 | Download |
| Thin Film (NEW) | ERA*V/K | 0402 to 0805 | 0.1 to 0.25 | 47 to 750 k | ±0.05, ±0.1 | Download | |
| Thick Film | ERJPB | 0603, 0805 | 0.2, 0.25 | 200 to 1M | ±0.1, ±0.5 | Download | |
| Current Sensing | Thick Film | ERJ*B / BW / LW | 0402 to 2512 | 0.1 to 1 | 5m to 9.1 | ±0.5 to ±5 | Download |
| Wide Terminal | ERJA / B | 0508 to 1225 | 0.33 to 2 | 5m to 1M | ±1, ±2, ±5 | Download | |
| Wide Terminal | ERJD | 0612, 1020 | 1, 2 | 10m to 200m | ±1, ±5 | Download | |
| Metal Plate | ERJMB / MS | 1020, 2512 | 2, 3 | 1m to 10m | ±1 | Download | |
| High temperature (NEW) | Thick film | ERJH | 0402 to 0805 | 0.1 to 0.5 | 1 to 300 k | ±0.5, ±1, ±5 | Download |
| High power | Anti-Surge | ERJP | 0402 to 1210 | 0.2 to 0.66 | 1 to 10M | ±0.5, ±1, ±5 | Download |
| Anti-Pulse | ERJT | 0805 to 1210 | 0.25 to 0.50 | 1 to 1M | ±5, ±10, ±20 | Download | |
| Anti-sulfurated | Thick Film | ERJS / U | 0201 to 2512 | 0.05 to 1 | 0.1 to 10M | ±0.5, ±1, ±2, ±5 | Download |
| Thick Film / Precision |
ERJU-R | 0402 to 0805 | 0.1, 0.125 | 100 to 100k | ±0.5 | Download | |
| Anti-Surge | ERJUP | 0805, 1206 | 0.5, 0.66 | 1 to 10M | ±0.5 to ±5 | Download | |
| Wide Terminal | ERJC1 | 1020 | 2 | 10m to 1 | ±1, ±5 | Download | |
| General purpose | Thick Film / Precision |
ERJ | 01005 to 2512 | 0.05 to 1 | 1 to 2.2M | ±0.5, ±1 | Download |
| Thick Film | ERJ | 01005 to 2512 | 0.031 to 1 | 1 to 10M | ±5, Jumper | Download | |
| Resistor Network | Network | EXB (8,15 element) |
1206 to 2512 | 0.025 to 0.063 /element |
47 to 1M | ±5 | Download |
| Array | EXB (2,4,8 element) |
0302 to 2009 | 0.03, 0.063, 0.1 /element |
1 to 1M | ±5 | Download | |
| Anti-sulfurated Array |
EXBU (2,4,8 element) |
0302 to 1506 | 0.03, 0.063 /element |
1 to 1M | ±5 | Download | |
Download our promotion documents
| Name | Size | Date | Language |
|---|---|---|---|
| Building Automation - Energy Management Solutions | 1 MB | 01.03.2022 | English |
| EV Charging Solutions from Panasonic Industry.pdf | 3 MB | 25.10.2023 | English |
| Name | Size | Date | Language |
|---|---|---|---|
| Products Catalog (Fixed Resistors) | 12 MB | 08.11.2023 | English |
| Devices & Solutions catalogue | 12 MB | 02.09.2025 | English |
| Name | Size | Date | Language |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Power Anti-Surge Chip Resistors: ERJP Series | 941 KB | 08.07.2024 | English |
| High Power Current Sensing Resistors: ERJD1 / ERJD2 Series | 425 KB | 08.07.2024 | English |
| Name | Size | Date | Language |
|---|---|---|---|
| AEC-Q200 Passive Components Selection Guide.pdf | 1 MB | 18.12.2025 | English |
| High Power SMD Resistors - Ideal for your downsizing | 384 KB | 19.02.2025 | English |
| High precision thin film resistors flyer | 767 KB | 16.07.2025 | English |
| Panasonic Focus 8 colors flyer | 650 KB | 02.09.2025 | English |
Videos
Questions and Answers about Resistors
Question: What is its failure mode?
Answer: The capacitor under normal service conditions is basically in open mode (in which the resistance increases). However, under harsh service conditions, it may operate in short mode (in which the resistance decreases).
For more detailed information on this subject, see the following pages: Chip Resistors - Failure by Usage Environment and Failure Mode
Question: What is migration mechanism?
Answer: Migration is generally a phenomenon occurring with a pair of electrodes placed in a high humidity environment. When voltage is applied between these electrodes, the anode metal is ionized and moves to the facing cathode and regenerates as metal again. The metal generated on the cathode grows into a tree-like shape and reduces insulation between poles, eventually causing a short-circuit.
Migration generally occurs when the three factors of electricity, water and halogen substance co-exist, by generating “Sn migration” on the exterior (solder) of the electronic component and “Ag migration” generated within the component.
As the Ag electrode is fully covered with a protective membrane or plating, Ag migration isn’t generated in a normal operating environment. But when halogen substances (F, Cl, Br) contained in flux etc. attaches with an active force, it causes deterioration of the protective membrane, and when moisture and an electric potential exists, migration may be happened.
Question: How can we avoid migration?
Answer: The following two methods can be applied for preventing migration.
- Remove halogen substance residue with a non-halogen cleaning agent.
- When using flux or adhesive, use the appropriate heat treatment* to make halogen substances inactive.
Question: What is mechanism of electrolytic corrosion?
Answer: When a halogen substance (F, Cl, Br) residue, contained in flux, adhesive, or cleaning agent, attaches to the surface of a chip resistor, and is exposed to a sulfur-containing atmosphere, the chip resistor surface protection membrane deteriorates, and moisture in the atmosphere containing halogen and sulfur tends to penetrate in the resistive element.
As thin-film chip resistors use a nickel-chrome alloy (Ni-Cr), the resistor element can be corroded by the penetrating moisture containing halogen and sulfur, leading to a resistance value increase and open circuit (wire breakage).
Thick film chip resistors consist of a resistive element made from a sintered mixture of ruthenium oxide and glass, and therefore free from electrolytic corrosion.